The hike in the banking malware this year is no doubt almost double compared to the previous one, and so in the techniques of malware authors.
Until now, we have seen banking Trojans affecting the infected device and steal users’ financial credentials in order to run them out of their money. But nowadays, malware authors are adopting more sophisticated techniques in an effort to target as many victims as they can.
BANKING MALWARE WITH NETWORK SNIFFING
Security researchers from the Anti-virus firm Trend Micro have discovered a new variant of banking malware that not only steal the users’ information from the device it has infected but, has ability to “sniff” network activity to steal sensitive information of other network users as well.
The banking malware, dubbed as EMOTET spreads rapidly through spammed emails that masquerade itself as a bank transfers and shipping invoices. The spammed email comes along with a link that users easily click, considering that the emails refer to financial transactions.
Once clicked, the malware get installed into users’ system that further downloads its component files, including a configuration and .DLL file. The configuration files contains information about the banks targeted by the malware, whereas the .DLL file is responsible for intercepting and logging outgoing network traffic.
The .DLL file is injected to all processes of the system, including web browser and then “this malicious DLL compares the accessed site with the strings contained in the previously downloaded configuration file, wrote Joie Salvio, security researcher at Trend Micro.
“If strings match, the malware assembles the information by getting the URL accessed and the data sent.”
ENCRYPTED STOLEN DATA
Meanwhile, the malware stores stolen data in the separate entries after been encrypted, which means the malware can steal and save any information the attacker wants.
“The decision to storing files and data in registry entries could be seen as a method of evasion“, Salvio said. “Regular users often do not check registry entries for possibly malicious or suspicious activity, compared to checking for new or unusual files. It can also serve as a countermeasure against file-based AV detection for that same reason.”
HTTPS CONNECTIONS KICKED
Moreover, the malware also has capability to even bypass the secure HTTPs connection which poses more danger to users’ personal information and banking credentials, as users will feel free to continue their online banking without even realizing that their information is being stolen.

“[It has] capability to hook to the following Network APIs to monitor network traffic: PR_OpenTcpSocket PR_Write PR_Close PR_GetNameForIndentity Closesocket Connect Send WsaSend”
This kind of financial threat is really dangerous for the people, because previous banking malwares often rely on form field insertion or phishing pages to steal users’ financial information, but the use of network sniffing in the malware, makes the threat even more harder for users to detect any suspicious activity as no changes are visibly seen, said the researcher.
Researchers are still investigating that how the gathered stolen data the malware sniffs from the network is being sent to the attacker.
The malware infection is not targeted to any specific region or country but, EMOTET malware family is largely infecting the users of EMEA region, i.e. Europe, the Middle East and Africa, with Germany on the top of the affected countries.
Users are advised to do not open or click on links and attachments provided in any suspicious email, but if the message is from your banking institution and of concern to you, then confirm it twice before proceeding.
The hike in the banking malware this year is no doubt almost double compared to the previous one, and so in the techniques of malware authors.
Until now, we have seen banking Trojans affecting the infected device and steal users’ financial credentials in order to run them out of their money. But nowadays, malware authors are adopting more sophisticated techniques in an effort to target as many victims as they can.
BANKING MALWARE WITH NETWORK SNIFFING
Security researchers from the Anti-virus firm Trend Micro have discovered a new variant of banking malware that not only steal the users’ information from the device it has infected but, has ability to “sniff” network activity to steal sensitive information of other network users as well.
The banking malware, dubbed as EMOTET spreads rapidly through spammed emails that masquerade itself as a bank transfers and shipping invoices. The spammed email comes along with a link that users easily click, considering that the emails refer to financial transactions.
Once clicked, the malware gets installed into users’ system that further downloads its component files, including a configuration and .DLL file. The configuration files contains information about the banks targeted by the malware, whereas the .DLL file is responsible for intercepting and logging outgoing network traffic.
The .DLL file is injected to all processes of the system, including web browser and then “this malicious DLL compares the accessed site with the strings contained in the previously downloaded configuration file, wrote Joie Salvio, security researcher at Trend Micro. “If strings match, the malware assembles the information by getting the URL accessed and the data sent.”
ENCRYPTED STOLEN DATA
Meanwhile, the malware stores stolen data in the separate entries after been encrypted, which means the malware can steal and save any information the attacker wants.
“The decision to storing files and data in registry entries could be seen as a method of evasion“, Salvio said. “Regular users often do not check registry entries for possibly malicious or suspicious activity, compared to checking for new or unusual files. It can also serve as a countermeasure against file-based AV detection for that same reason.”
HTTPS CONNECTIONS KICKED
Moreover, the malware also has capability to even bypass the secure HTTPs connection which poses more danger to users’ personal information and banking credentials, as users will feel free to continue their online banking without even realizing that their information is being stolen.
“[It has] capability to hook to the following Network APIs to monitor network traffic: PR_OpenTcpSocket PR_Write PR_Close PR_GetNameForIndentity Closesocket Connect Send WsaSend”
This kind of financial threat is really dangerous for the people, because previous banking malwares often rely on form field insertion or phishing pages to steal users’ financial information, but the use of network sniffing in the malware, makes the threat even more harder for users to detect any suspicious activity as no changes are visibly seen, said the researcher.
Researchers are still investigating that how the gathered stolen data the malware sniffs from the network is being sent to the attacker.
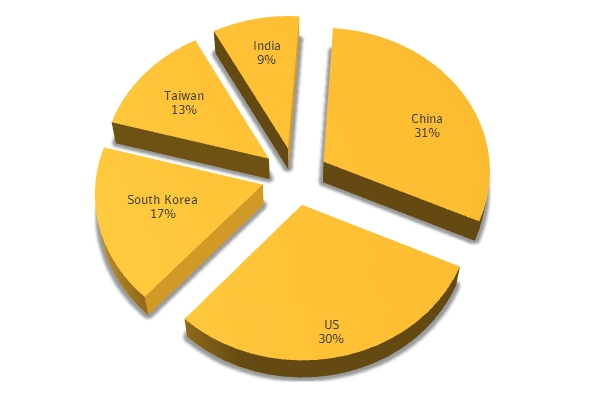
MALWARE DISTRIBUTION OVER WORLD MAP
The malware infection is not targeted to any specific region or country but, EMOTET malware family is largely infecting the users of EMEA region, i.e. Europe, the Middle East and Africa, with Germany on the top of the affected countries.
Users are advised to do not open or click on links and attachments provided in any suspicious email, but if the message is from your banking institution and of concern to you, then confirm it twice before proceeding.
IF INFECTED Visit Our Main Site OR call 754-234-5598
for latest computer repair and online news.
Local and Online Virus removal and computer repairs anytime, anywhere