Ransomware and other cyberthreats often go unseen by traditional detection methods like antivirus, deep packet inspection (DPI) or sandboxing. In fact, a report by Lastline Labs indicates that 51% of zero-day malware—threats that strike before developers have time to release a patch—is undetected by anti-virus solutions. So what can security professionals do to stop attacks? The answer lies, in part, in DNS.
One of the most powerful ransomware threats currently targeting individuals and organizations is Locky, which infects up to 100,000 devices per day, of which 3% submit payments. Cybersecurity experts estimate that Locky possesses 17% of the entire global market share for all ransomware infections.
First, let’s look at a few statistics that demonstrate the power and expense of Locky:
- Number of malicious email attachments delivered by Locky in Q2 2016 = 7 in 10
- The average ransom demand = $459
- Number of file types that can be encrypted by Locky (e.g., .docx, .jpeg, .xlsx) = 160
- The largest Locky payout to date = $17,000
- Number of devices infected daily around the world = 90,000
- Average daily payout by Locky at the current bitcoin exchange rate = $1.6M
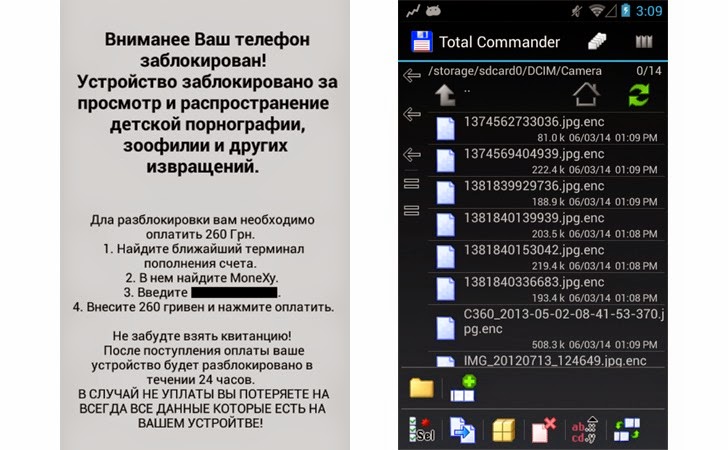
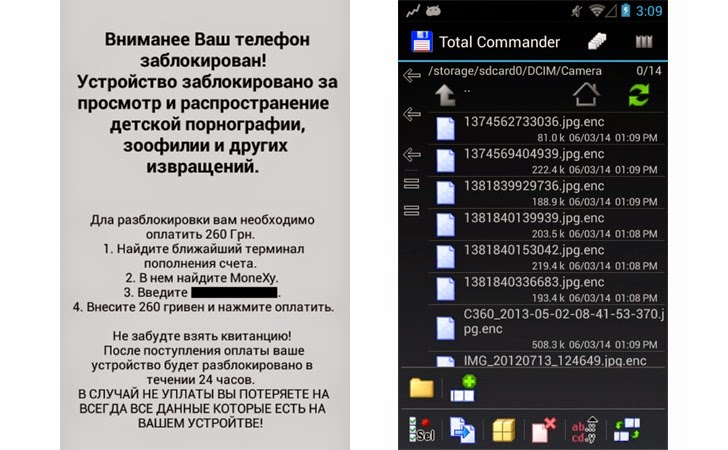
Locky is typically delivered through aggressive spam campaigns, often claiming to be an invoice. Despite the known dangers of clicking on links in unknown emails, Locky is so sly it entices even trained IT staff to click on obscure messages and activate downloads.
Once a download has completed, Locky connects with its Command & Control (C&C) server to get a cryptographic key to use for encryption. There are three known mechanisms for Locky to reach its C&C hosts:
- Direct IP communication
- A number of fixed domains
- A time-based Domain Generation Algorithm (DGA) that creates a set of random-looking domains that are only valid for a few days
Here is where DNS can play a role. DNS data can be analyzed to identify C&C connection mechanisms. When these communications are blocked, Locky’s ability to obtain encryption keys is limited, giving infected users a better chance of being protected.
Unfortunately, the DGA used by Locky to generate domains and get encryption keys is marked with the current time period combined with a secret seed, making it harder to block new domains quickly. Locky changes seeds frequently, and reverse engineering current versions of the malware to discover each new seed takes time. Every new seed indicates another wave in the life of the exploit, so until there is an accurate way to identify traffic associated with Locky, it can’t be permanently blocked.
But examination of a worldwide feed of anonymized DNS queries, along with anomaly detection and correlation technology, makes it possible to identify suspected domains used by Locky to download encryption keys in real time. ForcePoint is one company that has done some work to reverse engineer the DGA used by Locky. By using the existing DGA and conducting some additional processing of suspect domains, it is possible to determine new seeds used by Locky, thereby enumerating all future new domains Locky will use.
Below is a sampling of more recent domains created by Locky as detected by our DNS algorithms:
- mrjuvawlwa[.]xyz
- uydvrqwgg[.]su
- uwiyklntlxpxj[.]work
- owvtbqledaraqq[.]su
- udfaexci[.]ru
- eabfhwl[.]ru
- olyedawaki[.]pl
- uxwfukfqxhydqawmf[.]su
- ikdcjjcyjtpsc[.]work
- wrbwtvcv[.]su
- osxbymbjwuotd[.]click
- qtuanjdpx[.]info
As Locky and other types of ransomware become more adept at avoiding detection and remediation, new strategies need to be used to combat them. Many of the new cyberthreat strategies make traditional malware block lists less effective. Facing DGAs with fast-changing seeds, security researchers must constantly identify the new seeds used by each wave of phishing to pre-generate domains. Once new seeds are released the old ones immediately become obsolete.
By utilizing a broad set of DNS query data, it is possible to detect and track the evolution of generated domains through a variety of algorithmic methods such as clustering, reputation scoring, reverse engineering and additional methods that continuously evolve. Recent innovations include anomaly detection algorithms, new domain clustering and a Domain Reputation System that resulted in almost 100,000 domains and C&Cs provisioned daily for blocking.
By employing these advanced methods, suspicious domains can be detected with a high level of accuracy very quickly, and false positives can also be weeded out so good traffic can still reach legitimate sites. Currently, this is the best defense against Locky. Service providers and companies can use this technique to protect their online users from having their files encrypted, and identify machines that have been infected.
Locky provides ample evidence that attackers are continuously innovating. Staying one step ahead requires cybersecurity expertise and real-time processing of massive, worldwide data sets to uncover malicious activity. Blocking traffic to these domains is a good way to avoid the threat of Locky, and expert security teams that take the right steps to understand its behavior and put appropriate measures in place to protect would-be victims will render cyberthreats much less effective.